How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into every aspect of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight techniques and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll cover essential controls, camera operation, battery management, and even navigating complex airspace regulations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will explore the intricacies of drone flight, covering topics ranging from understanding basic controls and navigating different flight modes to mastering advanced techniques like waypoint missions and cinematic aerial filming. The guide also emphasizes the importance of safety, responsible operation, and adherence to all relevant regulations. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to operate a drone and capture stunning aerial footage.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures

Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, understanding local regulations, and briefing yourself on emergency procedures. Failing to do so can lead to accidents and legal repercussions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is essential to identify any potential issues before takeoff. This involves visually checking all components for damage or wear and tear. The following table Artikels key inspection points:
| Item | Check | Action Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, chips, or damage | Replace damaged propellers | Ensure all propellers are securely fastened. |
| Motors | Check for loose screws or damage | Tighten loose screws; replace damaged motors | Listen for unusual noises during a pre-flight motor test. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition | Charge battery if necessary; replace if damaged or swollen | Avoid using damaged or old batteries. |
| Camera | Check lens for dirt or debris | Clean lens gently with a microfiber cloth | Ensure the camera is securely mounted. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if necessary | Sufficient satellites are required for stable flight. |
| Gimbal | Check for smooth movement and proper calibration | Recalibrate gimbal if necessary | A properly functioning gimbal ensures stable footage. |
| Airframe | Inspect for any cracks, damage, or loose parts | Repair or replace damaged parts | Ensure all parts are securely fastened. |
| Remote Controller | Check battery level and functionality | Charge remote if necessary | Ensure all buttons and sticks are responsive. |
Understanding Local Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires adhering to local laws and regulations. Ignoring these rules can result in hefty fines, legal action, or even jail time. For example, flying near airports without proper authorization is strictly prohibited and can have serious consequences. Always check with your local aviation authority (e.g., FAA in the US, CAA in the UK) for specific rules and regulations in your area.
These regulations often dictate maximum flight altitudes, restricted airspace zones, and required registration procedures.
Drone Safety Briefing for New Operators
A safety briefing is crucial for new drone pilots. It should cover potential hazards like collisions with objects, loss of control, and battery failure. Emergency procedures, such as how to regain control in a difficult situation or execute an emergency landing, should be thoroughly explained. The briefing should also emphasize the importance of responsible operation and respect for privacy.
Safe Drone Operation in Various Weather Conditions
Weather significantly impacts drone flight. Strong winds, rain, or snow can severely affect stability and control. The following checklist summarizes safe operating practices in different weather conditions:
- No Wind/Light Wind: Ideal conditions for flight. Ensure a clear and open area.
- Moderate Wind: Flight is possible, but exercise caution. Reduce flight speed and be prepared for wind gusts.
- Strong Wind: Avoid flying. Strong winds can cause loss of control and damage to the drone.
- Rain/Snow: Avoid flying. Moisture can damage electronic components.
- Fog/Low Visibility: Avoid flying. Reduced visibility increases the risk of collisions.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
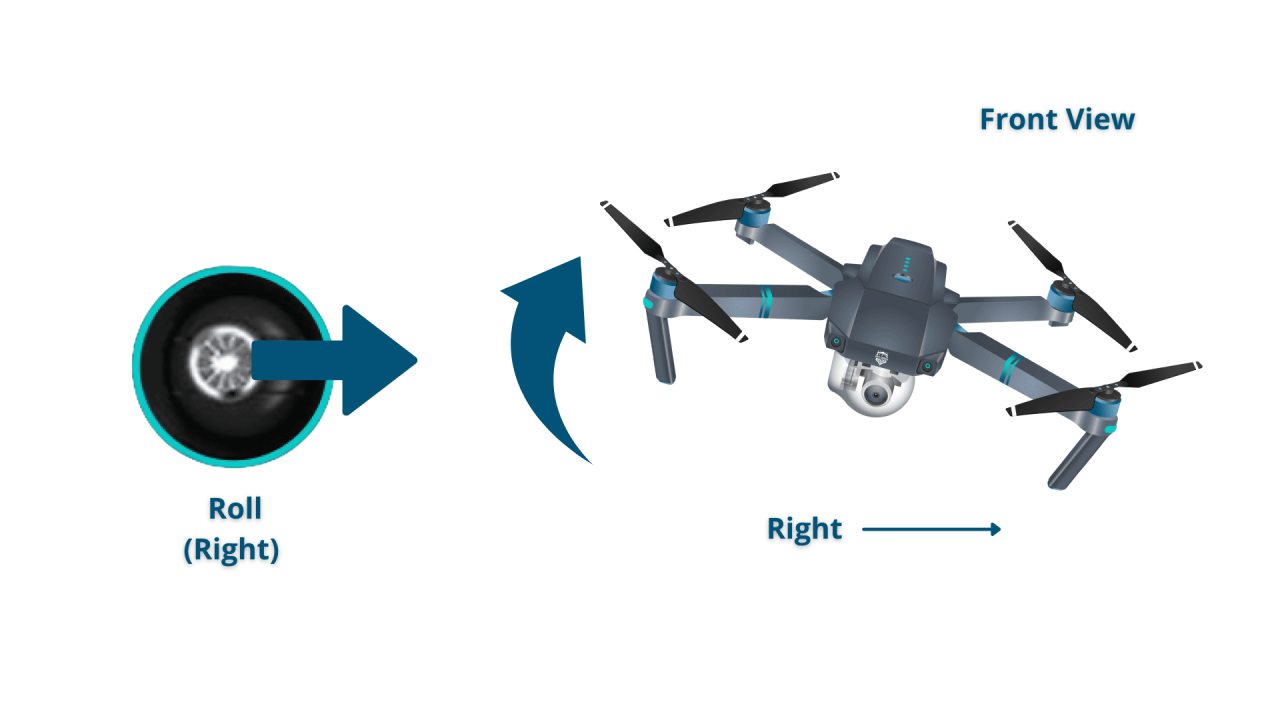
Mastering drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Understanding the functions of each control stick and button on your remote is essential for precise maneuvering.
Drone Control Stick and Button Functions
- Left Stick (Yaw/Throttle): Controls drone rotation (yaw) and altitude (throttle).
- Right Stick (Pitch/Roll): Controls the drone’s forward/backward (pitch) and left/right (roll) movement.
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates an automated return to the takeoff point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Cuts power to the motors, causing an immediate descent.
- Camera Control Buttons: Used to adjust camera settings, take photos, and start/stop video recording.
- Flight Mode Selection Button: Allows switching between different flight modes (e.g., GPS, Attitude).
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing a Drone
- Takeoff: Gently push the throttle stick upwards to initiate ascent. Maintain a steady, slow ascent.
- Hovering: Once at the desired altitude, maintain a steady throttle position to keep the drone hovering in place.
- Landing: Gently lower the throttle stick to initiate descent. Maintain a slow and controlled descent until the drone touches down.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. Understanding their applications is crucial for safe and effective operation.
| Flight Mode | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Relies on GPS signals for position holding and stability. | Ideal for stable hovering and long-range flights. |
| Attitude Mode | Maintains the drone’s attitude (orientation) relative to its initial position. | Useful for precise maneuvers in confined spaces where GPS signal might be weak. |
| Sport Mode (if available) | Provides increased responsiveness and speed. | Suitable for experienced pilots in open areas with good visibility. |
Precise Drone Maneuvering and Wind Compensation

Precise maneuvering requires practice and understanding of wind effects. To counteract wind, adjust the control sticks to compensate for wind gusts. Practice flying in different wind conditions to develop your skills.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The drone’s camera is a key feature, allowing for stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is essential for capturing high-quality images.
Drone Camera Settings and Their Impact on Image Quality
Camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO significantly affect image quality. Aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens, influencing depth of field. Shutter speed determines how long the sensor is exposed to light, affecting motion blur. ISO controls the sensor’s sensitivity to light, impacting image noise.
Achieving Different Camera Angles and Perspectives
The drone’s ability to move freely in three dimensions allows for creative camera angles. Tilting the camera up or down, and adjusting the drone’s position, enables capturing diverse perspectives.
Using Drone Camera Features
Modern drones offer features like zoom, focus adjustments, and different recording modes (photo, video, timelapse). Familiarize yourself with these features to maximize your creative potential.
Composing Visually Appealing Aerial Shots
Applying principles of composition, such as the rule of thirds and leading lines, enhances the visual appeal of aerial shots. Framing your subject effectively creates visually engaging images.
Drone Battery Management and Maintenance: How To Operate A Drone
Proper battery care is essential for maximizing flight time and ensuring the longevity of your drone’s battery. Neglecting battery maintenance can lead to reduced performance and potential safety hazards.
Proper Battery Care and Charging Procedures
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging or discharging the battery, as this can damage it. Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
Monitoring Battery Health and Identifying Signs of Wear and Tear
Regularly check the battery’s voltage and capacity. Signs of wear include reduced flight time, swelling, or unusual heating during charging or use. Replace worn-out batteries promptly.
Safe Storage and Transportation of Drone Batteries
Store batteries in a protective case to prevent damage and short circuits. When transporting batteries, follow all relevant safety regulations, often involving specific packaging requirements.
Extending Battery Life and Maximizing Flight Time
To extend battery life, avoid extreme temperatures, fully charge before each flight (but avoid overcharging), and store batteries at optimal levels (around 50% charge) when not in use. Flying in calm conditions also contributes to longer flight times.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. Understanding common issues and their solutions is vital for resolving problems efficiently and safely.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal considerations, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. Proper training is essential for safe and responsible drone operation.
Identifying Common Drone Malfunctions
- GPS Signal Loss: The drone loses its GPS connection, resulting in erratic flight or inability to hold position.
- Low Battery Warning: The drone’s battery is running low, requiring an immediate landing.
- Motor Failure: One or more motors malfunction, causing loss of control or unstable flight.
- Gimbal Malfunction: The camera gimbal becomes unresponsive or experiences erratic movement.
- Remote Controller Issues: The remote controller loses connection with the drone or malfunctions.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Malfunctions
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific issue. Consult your drone’s manual for detailed instructions. Common steps may include restarting the drone, recalibrating the compass, checking battery levels, or contacting customer support.
Performing Basic Drone Maintenance, How to operate a drone
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning propellers and inspecting the airframe for damage, is crucial for preventing malfunctions. Clean the drone’s body and propellers gently with a soft cloth and compressed air.
Safely Recovering a Drone After a Crash
If a crash occurs, prioritize safety. Assess the damage and ensure the area is safe before attempting recovery. Carefully inspect the drone for damage before attempting another flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively pilot your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, ensuring you’re well-prepared before taking to the skies.
Ultimately, responsible operation of a drone depends on thorough preparation and understanding.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Beyond basic operation, advanced techniques enhance the capabilities of your drone, enabling more complex and creative flights.
Using Waypoint Missions for Automated Flight
Waypoint missions allow for pre-programmed flight paths. The pilot defines a series of waypoints, and the drone autonomously follows the planned route. This is useful for repetitive tasks like aerial inspections or surveying.
For example, a construction site inspection might involve setting waypoints around the perimeter of the site, allowing the drone to capture images or video of the entire area without manual control.
Capturing Smooth Cinematic Aerial Footage
Smooth cinematic footage requires careful planning and execution. Techniques such as using a gimbal, maintaining slow and steady movements, and planning shots with smooth transitions are crucial.
Comparing and Contrasting Different Drone Models and Their Capabilities
Different drone models offer varying features and capabilities. Factors to consider include camera quality, flight time, range, and advanced features like obstacle avoidance.
Designing a Flight Plan for a Specific Scenario
A flight plan for filming a construction site, for instance, would involve identifying safe flight zones, determining the necessary camera angles, and planning the flight path to capture all relevant areas. Similarly, inspecting a bridge would require a plan focusing on close-up shots of structural elements while maintaining a safe distance.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that blends technology, skill, and a deep respect for safety regulations. From the initial pre-flight checklist to the thrill of capturing breathtaking aerial perspectives, each step contributes to a holistic understanding of this exciting technology. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of drone operation, but continued practice and exploration will further hone your skills and expand your capabilities.
Remember always to prioritize safety, respect airspace restrictions, and embrace the creative possibilities that drone technology offers.
FAQ
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automatic features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How do I obtain necessary permits or licenses to fly a drone?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific requirements and registration processes. In many places, registration is required before flying.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency stop or return-to-home function. If unsuccessful, attempt to visually track its location and contact local authorities if it poses a safety hazard.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s best practice to calibrate the compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a significantly different location.